Laboratory glassware is essential for scientific experiments, offering precise tools for measuring, mixing, and heating substances. This guide provides names, pictures, and descriptions to help identify and use lab equipment effectively.
Overview of Common Laboratory Glassware
Common laboratory glassware includes beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, graduated cylinders, pipettes, and volumetric flasks. Beakers are used for holding and mixing liquids, while Erlenmeyer flasks are ideal for heating substances due to their narrow necks. Graduated cylinders measure precise liquid volumes, and pipettes transfer small, accurate amounts. Volumetric flasks are designed for preparing solutions with exact volumes. Accessories like clamps, rings, and stands provide support during experiments. These tools are made from durable materials, such as borosilicate glass, ensuring chemical resistance and thermal stability. Understanding their functions and proper usage is crucial for safe and efficient laboratory operations. This overview highlights the essential glassware needed for fundamental lab tasks, aiding in accurate measurements, mixing, and solution preparation.
Importance of Knowing Lab Glassware Names and Uses
Knowing the names and uses of lab glassware is crucial for conducting experiments safely and efficiently. Proper identification ensures accurate measurements, reduces errors, and prevents contamination. For instance, using a volumetric flask instead of a beaker for precise volume measurements is essential. Familiarity with glassware like pipettes and graduated cylinders ensures precise liquid handling. Misusing equipment can lead to inaccurate results or safety hazards. Understanding each tool’s purpose enhances experimental outcomes and adherence to safety protocols. This knowledge is vital for both novice and experienced scientists, forming the foundation of reliable laboratory practices and scientific discovery.

Basic Laboratory Glassware
Basic lab glassware includes essential tools like beakers, flasks, cylinders, funnels, and pipettes. These items are versatile and fundamental for experiments, mixing, measuring, and heating substances in labs.
Beakers
Beakers are essential laboratory glassware used to hold and mix liquids. They are available in various sizes, typically ranging from 50ml to 2000ml. Unlike graduated cylinders, beakers are not meant for precise measurements but are ideal for containing and transferring substances. They often feature a spout for easy pouring and may have markings for approximate volume estimation. Beakers are durable, easy to clean, and suitable for both hot and cold liquids. They are a fundamental tool in chemistry, biology, and other scientific disciplines, serving as a versatile container for everyday laboratory tasks. Proper handling and storage ensure their longevity and safety in the lab environment.
Erlenmeyer Flasks
Erlenmeyer flasks are a type of laboratory glassware characterized by their conical shape, wide mouth, and narrow neck. They are ideal for mixing, heating, and boiling liquids, as their shape minimizes splashing. Available in various sizes, they often feature a marking spot for labeling. Unlike beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks are not graduated for precise measurements but are excellent for containing reactions. They are commonly used in titrations and are compatible with laboratory clamps for secure heating. Their durability and chemical resistance make them a staple in chemistry labs. Proper handling, such as avoiding overheating beyond 420°C, ensures their longevity. Erlenmeyer flasks are versatile tools for both routine and specialized laboratory procedures, offering reliability and precision in scientific work.
Graduated Cylinders
Graduated cylinders are transparent, cylindrical glassware used to accurately measure and transfer liquid volumes. They feature calibrated markings along their height, enabling precise quantification. Available in various sizes, from 10ml to 2000ml, they are ideal for routine laboratory tasks requiring volume measurement. Unlike beakers, graduated cylinders provide exact measurements, making them essential for titrations, dilutions, and mixing solutions. Proper handling involves reading the meniscus and using appropriate techniques to pour liquids. Cleaning is crucial to maintain accuracy, and they should be stored upright to prevent breakage. Graduated cylinders are indispensable tools in chemistry labs, offering reliability and precision in scientific experiments and procedures, ensuring accurate results in various applications, from education to research settings. Their clarity and durability make them a fundamental component of laboratory equipment;
Funnels
Funnels are cone-shaped laboratory tools designed to direct liquids or small solid particles into containers with narrow openings, minimizing spills. They are typically made of glass, plastic, or stainless steel, offering durability and chemical resistance. Funnels are versatile, used in filtration, transfers, and mixing processes. Glass funnels are commonly used in chemistry labs for their transparency, allowing easy observation of the flow. They come in various sizes to accommodate different applications, from small-scale experiments to large industrial processes. Proper placement and alignment are crucial to ensure safe and efficient use. Funnels are indispensable in laboratories for precise and mess-free transfers, making them a fundamental tool in scientific workflows and experiments. Their simplicity and functionality make them a cornerstone of lab equipment, essential for maintaining order and safety during procedures.
Pipettes
Pipettes are precision instruments used to measure and transfer small, accurate volumes of liquids in laboratory settings. They are available in various types, including glass and plastic models, each designed for specific applications. Glass pipettes are durable and chemically inert, making them ideal for handling corrosive substances. Plastic pipettes are often used for less demanding tasks and are disposable, reducing contamination risks. Pipettes are categorized by volume, ranging from microliter to larger capacities, ensuring precise measurements. They are essential for titrations, solution preparations, and other delicate procedures. Proper technique is crucial to avoid errors and ensure accurate results. Regular calibration and maintenance are necessary to uphold their precision and functionality, making pipettes indispensable tools in scientific research and experimentation. Their role in laboratories is vital for achieving reliable and consistent outcomes in various scientific endeavors.

Specialized Laboratory Glassware
Specialized glassware includes tools like volumetric flasks, test tubes, and crucibles, designed for specific tasks such as precise measurements, sample testing, and high-temperature experiments, enhancing lab efficiency and accuracy.
Volumetric Flasks
A volumetric flask is a precise laboratory tool used to prepare solutions to a known, fixed volume. It features a single graduation mark, ensuring accuracy in measurements. Made from high-quality borosilicate glass, these flasks are chemically inert and resistant to thermal shock. They are commonly used in titrations, standard solutions, and accurate dilutions; Available in various sizes, volumetric flasks are essential for quantitative analysis. The neck is designed for easy labeling, and some modern versions include QR codes for quick access to product information. Proper handling and calibration are crucial to maintain their precision. Widely used in chemistry, biology, and pharmaceutical labs, volumetric flasks are a cornerstone of scientific instrumentation.
Test Tubes
Test tubes are cylindrical glass vessels used to hold small quantities of substances for experiments and observations. They are typically 10-20 cm long with open ends and rounded bottoms; Made from borosilicate glass, they are heat-resistant and durable. Test tubes are used for mixing, heating, and storing chemicals, as well as for conducting chemical reactions. They often have markings for labeling. Available in various sizes, they are a fundamental tool in chemistry and biology labs. Proper handling is essential to avoid breakage. Test tubes are widely used in educational settings for demonstrations and student experiments. Their versatility makes them indispensable in scientific research and routine laboratory procedures. Regular cleaning ensures they remain contamination-free for accurate results.
Evaporating Dishes
Evaporating dishes are shallow, wide-mouthed glassware used to evaporate liquids or heat solids at low temperatures. They typically have a flat bottom and curved sides, making them ideal for containing substances during heating. Made from heat-resistant glass, they can withstand moderate heat without breaking. These dishes are commonly used in laboratories to concentrate solutions or dry solids. They are also used for heating substances that require gentle warming. Evaporating dishes come in various sizes and are easy to clean, ensuring they remain free from contamination. Proper handling and storage are essential to maintain their integrity. They are a fundamental tool in chemistry labs for processes involving evaporation and heating. Regular maintenance ensures they remain durable and effective for laboratory use. Their design allows for even heat distribution, making them versatile for various scientific applications;
Watch Glasses
Watch glasses are small, circular, and flat pieces of glassware used primarily to hold solids during weighing or heating. They are typically placed on a balance or over a flask to catch residues. Their flat design allows for easy placement on laboratory surfaces. Watch glasses are made from heat-resistant glass, making them suitable for heating small samples. They are also used to cover crucibles or evaporating dishes to prevent contamination. Available in various sizes, watch glasses are versatile tools in chemistry labs. Proper handling and storage are essential to avoid breakage. They are simple yet essential accessories for laboratory procedures. Regular cleaning ensures they remain contamination-free. Their durability and heat resistance make them a must-have for various scientific tasks. Watch glasses are indispensable for accurate and safe laboratory operations.
Crucibles
Crucibles are small, heat-resistant containers made of materials like porcelain, quartz, or metal, designed to withstand high temperatures. They are used for heating substances in laboratories, often during chemical analysis or synthesis. Crucibles have thick, sturdy walls to handle thermal stress and are commonly used for ash determination, ignition tests, or melting solids. They are available in various sizes and shapes, with some featuring lids to prevent splashing. Crucibles are essential for precise heating and containment, ensuring safe laboratory operations. Proper handling and cleaning are crucial to maintain their durability and prevent contamination; Crucibles are indispensable tools in chemistry and materials science for high-temperature experiments. Their versatility and heat resistance make them a fundamental part of laboratory setups. Regular inspection ensures they remain in good condition for repeated use. Crucibles are a cornerstone in scientific experimentation and analysis.

Lab Glassware Accessories
Lab glassware accessories like clamps, rings, stands, and supports are essential for securing and stabilizing equipment during experiments. They ensure safe handling and prevent damage or spills.
Clamps and Rings
Clamps and rings are vital accessories for securing laboratory glassware during experiments. Clamps are used to grip and hold items like flasks or beakers in place, while rings provide additional support and stability. They are commonly attached to stands or other fixed structures to prevent equipment from moving or breaking. These accessories are designed to handle various sizes and types of glassware, ensuring safe and efficient operation. Proper use of clamps and rings is essential to maintain control over setups, especially during heating or titration processes. They are available in different materials and sizes to suit specific laboratory needs, making them indispensable in any lab setting.
Stands and Supports
Stands and supports are essential for stabilizing laboratory glassware during experiments. They provide a sturdy base for equipment like beakers, flasks, and funnels, ensuring they remain upright and secure. Often used in conjunction with clamps and rings, these accessories prevent accidental spills and breakages. Stands are typically made of metal or durable plastic, offering adjustable features to accommodate various sizes of glassware. They are particularly useful for setups that require heating or precise control, such as distillations or titrations. By maintaining the integrity of the setup, stands and supports enhance safety and efficiency in the laboratory. Their versatility makes them a crucial component in any scientific workspace.
Safety and Care of Laboratory Glassware
Handle glassware with care to avoid breakage. Avoid heating above 420°C to prevent stress. Store properly, inspect for damage, and use gloves and goggles for protection.
Handling and Storage Tips
Proper handling and storage of lab glassware are crucial to maintain safety and functionality. Always inspect glassware for cracks or chips before use, as damaged items can break under stress. When handling, avoid using bare hands for hot or fragile pieces; wear gloves to prevent thermal burns and provide a secure grip. Store glassware in designated areas, such as shelves or cabinets, to protect it from accidental knocks. Separate items to prevent chipping, and use soft padding or dividers for delicate items. Never leave glassware unattended in open flames or extreme temperatures, as this can cause thermal shock and weakening of the glass structure. Regularly clean and dry glassware before storage to prevent chemical residue buildup, which can affect future experiments. Proper labeling of stored items ensures easy identification and minimizes mix-ups. By adhering to these guidelines, you can extend the lifespan of your lab glassware and ensure a safer working environment for everyone involved.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Proper cleaning and maintenance of lab glassware are essential to ensure accuracy, safety, and longevity. Wash glassware immediately after use to prevent chemical residues from hardening, which can make removal difficult. Use mild detergents and soft brushes to avoid scratching delicate surfaces. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals, as they can damage glass or leave residues. Rinse thoroughly with distilled water to remove all soap and chemical traces. Dry glassware with lint-free cloths or in a clean, dry environment to prevent water spots. For items like burettes and pipettes, disassemble and clean each part separately to ensure precision. Regular maintenance, such as checking for cracks or chips, helps prevent accidents and ensures reliable performance. Proper care extends the lifespan of your lab glassware and maintains experimental integrity.

Identifying Lab Glassware from Pictures
Visual recognition of lab glassware is key to learning and using equipment effectively. This section provides a guide with pictures and descriptions to help identify common glassware accurately.
Visual Recognition of Common Glassware
Visual recognition is a foundational skill for identifying lab glassware. By examining shapes, sizes, and features, one can distinguish tools like beakers, flasks, and pipettes. Beakers have straight sides, while Erlenmeyer flasks taper, aiding in pouring without spillage. Graduated cylinders feature markings for precise measurements, and volumetric flasks have a single graduation line for accurate solution preparation. Funnels are conical with a narrowed spout, and pipettes have precise measurement markings. Test tubes are narrow and cylindrical, often used for reactions. Evaporating dishes are shallow with a wide mouth, and watch glasses are flat for weighing solids. Crucibles are heavy-duty, heat-resistant, and used for high-temperature processes. Recognizing these features ensures correct tool selection and safe lab practices.
Using a PDF Guide for Identification
A PDF guide is an invaluable resource for identifying lab glassware, offering detailed images, names, and descriptions. These guides compile comprehensive lists of equipment, such as beakers, flasks, and pipettes, with clear visuals to aid recognition; Many PDFs include labeled diagrams, allowing users to match unknown items with their correct names and functions. They often cover both basic and specialized glassware, ensuring a wide range of tools are represented. Some guides also include QR codes or links to additional resources, enhancing the learning experience. By referring to a PDF guide, users can quickly identify glassware, understand its purpose, and ensure proper usage in laboratory settings. This makes them an essential tool for students, researchers, and lab professionals alike.
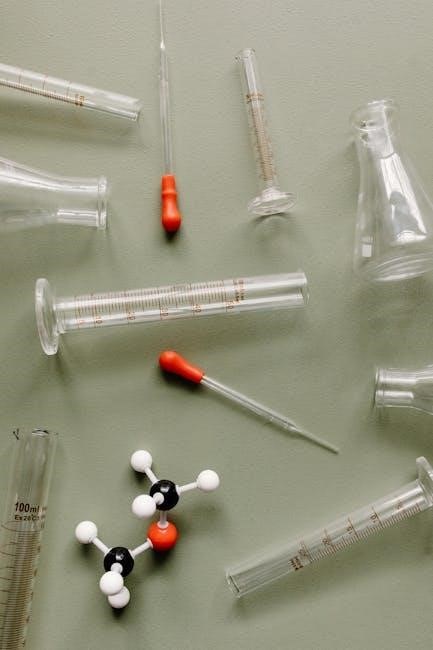
Creating a Lab Glassware PDF Guide
A comprehensive PDF guide compiles names, pictures, and descriptions of lab glassware, aiding in easy identification and understanding of their uses for scientific experiments and research.
Steps to Compile a Comprehensive Guide
Compiling a detailed lab glassware guide involves several key steps. First, gather high-quality images of each piece of equipment from reliable sources. Next, research and list the official names and their specific uses. Organize the content logically, starting with basic tools like beakers and graduated cylinders, then moving to specialized items such as volumetric flasks. Include descriptions of materials, sizes, and safety precautions. Use clear, concise language to ensure accessibility for all skill levels. Finally, format the guide into a PDF, ensuring it is visually appealing and easy to navigate. Regular updates will keep the information current and relevant for ongoing scientific needs.
Including Names, Pictures, and Descriptions
A comprehensive guide should include the names of each glassware item, accompanied by high-quality images for visual recognition. Detailed descriptions of their uses, materials, and sizes are essential. For example, a beaker is described as a cylindrical container for holding liquids, while an Erlenmeyer flask is noted for its conical shape, ideal for titrations. Safety tips, such as avoiding overheating glassware, should also be highlighted. This structured approach ensures that users can easily identify and understand the purpose of each tool, making the guide a valuable resource for both students and professionals in laboratory settings. Clear organization enhances usability and aids in quick reference during experiments.
Understanding lab glassware names, pictures, and uses is crucial for safe and effective experimentation. This knowledge enhances precision, safety, and efficiency in scientific workflows and discoveries.
Beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, and graduated cylinders are fundamental for measuring and mixing liquids. Pipettes ensure precise liquid transfers, while volumetric flasks prepare exact solutions. Test tubes and crucibles are used for heating and reactions. Evaporating dishes and watch glasses aid in solvent evaporation and sample handling. Funnels and clamps facilitate safe transfers and setups. Understanding these tools enhances lab efficiency and safety, making them indispensable for scientific workflows. This guide provides clear names, pictures, and descriptions to help identify and use each piece effectively, ensuring accuracy and confidence in laboratory practices.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Lab Glassware Knowledge
Mastering the names, functions, and proper use of lab glassware is crucial for scientific success. Correct identification and usage ensure precise measurements, safe experiments, and reliable results. Whether a student or researcher, this knowledge streamlines workflows and prevents errors. A comprehensive PDF guide with images and descriptions is invaluable for quick reference. Familiarity with tools like beakers, flasks, and pipettes fosters confidence and efficiency. Investing time to learn and maintain lab glassware is essential for advancing skills and achieving goals in chemistry and related fields. This foundation supports innovation and discovery, making it a cornerstone of scientific education and practice.
