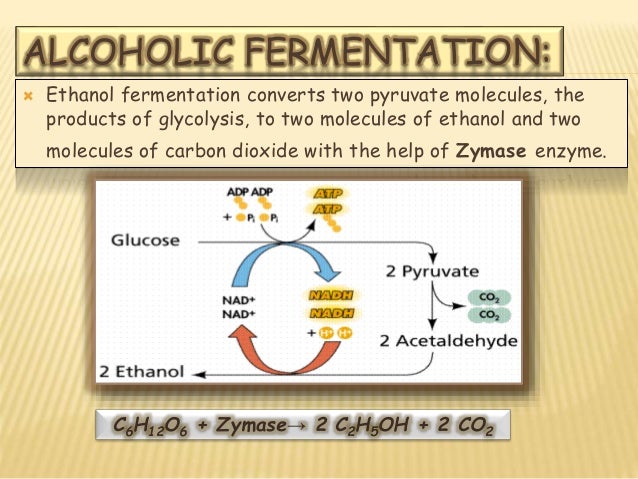
Fermentation / Anaerobic Respiration Biology Socratic Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation (which can result in yogurt and in sore muscles), and in decomposition of organic matter. The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol/lactic acid.
Anaerobic Respiration – TEL Library
Anaerobic Respiration Boundless Microbiology. 2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs, Anaerobic respiration multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), anaerobic respiration quiz answers pdf, O level biology learning for online degree programs. Anaerobic respiration quiz questions and answers pdf, only partial breakdown of glucose molecule ….
Anaerobic respiration, Respiratory quotient, Compensation point, Kuhne’s fermentation tube. The anaerobic breakdown of glucose to carbondioxide and ethanol is a form of respiration referred to fermentation. Compiler Design Notes CS8602 pdf free download. OBJECTIVES: CS8602 Notes Compiler Design To learn the various phases of compiler 2013-6-21 · Anaerobic Respiration In Yeast Name Date In biology, anaerobic respiration is a way for an organism to produce usable energy without the involvement of oxygen; it is respiration without oxygen. Respiration is a redox reaction that processes
2015-3-2 · Place the Gas Sensor, and start collecting the data. for 4 minutes. Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration Elissa Seidman Edwin Yu - The Marathon - If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? Practice Eat the right foods Drink the right liquids Aim: SWBAT: Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration. 2019-10-12 · Fermentation products contain chemical energy (they are not fully oxidized), but are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O 2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration.
Anaerobic respiration multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), anaerobic respiration quiz answers pdf, O level biology learning for online degree programs. Anaerobic respiration quiz questions and answers pdf, only partial breakdown of glucose molecule … 2013-10-11 · lactic acid during anaerobic fermentation Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO 4): Provides Mg2+ , a cofactor that activates some enzymes of glycolysis Sodium fluoride (NaF) – an inhibitor of some enzymes of glycolysis – inhibits phosphorylation Glucose – a common organic molecule used …
Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor. 2019-10-12 · Fermentation products contain chemical energy (they are not fully oxidized), but are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O 2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration.
Anaerobic respiration multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), anaerobic respiration quiz answers pdf, O level biology learning for online degree programs. Anaerobic respiration quiz questions and answers pdf, only partial breakdown of glucose molecule … 2010-10-22 · energy via the process of anaerobic respiration, also known as fermentation--but far less energy per glucose is extracted, since glucose cannot be fully broken down without oxygen. In today’s lab, you will work in teams of four and design an experiment in which you manipulate some factor affecting the rate of anaerobic metabolism in live yeast.
2015-3-2 · Place the Gas Sensor, and start collecting the data. for 4 minutes. Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration Elissa Seidman Edwin Yu - The Marathon - If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? Practice Eat the right foods Drink the right liquids Aim: SWBAT: Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration. In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to ethyl alcohol; during lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously
Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor. 2019-11-27 · Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. This is the currently selected item. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Regulation of cellular respiration. Practice: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation.
2018-12-13 · to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously and oxygen is scarce. Big Question: W hat is the fundamental difference between anaerobic cellular respiration and different 2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs
2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs Define anaerobic respiration. anaerobic respiration synonyms, anaerobic respiration pronunciation, anaerobic respiration translation, English dictionary definition of …
There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used; instead, organic or inorganic molecules are used as final electron acceptors. Fermentation includes processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH. Types of fermentation include lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation, in which ethanol is
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration (practice) Khan
Anaerobic Respiration – TEL Library. 2013-12-5 · Cellular Respiration: Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration is a process which happens inside the cells in which carbohydrates, especially glucose, is broken down for the energy to be released which can be used by the cells., 2019-11-26 · What is the difference between Fermentation and Anaerobic Respiration? • Fermentation is a process where energy is produced from organic compounds using endogenous electron acceptors, and there are many types of electron acceptors..
CARBOHYDRATE FERMENTATION TEST
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration Cellular. There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anaerobic_organisms 2012-11-21 · Fermentation or anaerobic respiration is a method that is used by yeast cells to produce energy, while producing the ethanol byproduct. Harnessing the natural power of yeast and anaerobic respiration, fuel companies produce billions of gallons of valuable ethanol. You will take on the role of.
In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to ethyl alcohol; during lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +.
2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs 2013-10-11 · lactic acid during anaerobic fermentation Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO 4): Provides Mg2+ , a cofactor that activates some enzymes of glycolysis Sodium fluoride (NaF) – an inhibitor of some enzymes of glycolysis – inhibits phosphorylation Glucose – a common organic molecule used …
The most important industrial fermentation is the anaerobic production of ethanol by S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. However, mixed-culture processes in anaerobic fermentation are also difficult to study and model. The microbial communities are usually unstable, varying with environmental changes and the availability of nutrients. The most important industrial fermentation is the anaerobic production of ethanol by S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. However, mixed-culture processes in anaerobic fermentation are also difficult to study and model. The microbial communities are usually unstable, varying with environmental changes and the availability of nutrients.
2018-12-13 · to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously and oxygen is scarce. Big Question: W hat is the fundamental difference between anaerobic cellular respiration and different 2019-11-27 · Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. This is the currently selected item. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Regulation of cellular respiration. Practice: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation.
The most important industrial fermentation is the anaerobic production of ethanol by S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. However, mixed-culture processes in anaerobic fermentation are also difficult to study and model. The microbial communities are usually unstable, varying with environmental changes and the availability of nutrients. 2018-8-29 · anaerobic digestion, oxygen is unavailable, respiration is incomplete and collectively termed anaerobic fermentation. During fermentation, sugars are degraded into molecules such as lactate, alcohol, butyrate, or propionate. Subsequently, butyrate and propionate can be used as substrate by methane-producers.
Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor. 2018-5-30 · process, called anaerobic cellular respiration, is performed by some bacteria and archaea. In this article, we'll take a closer look at anaerobic cellular respiration and at the different types of fermentation. Anaerobic cellular respiration Anaerobic cellular respiration is similar to aerobic cellular respiration in that electrons
Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor. Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used; instead, organic or inorganic molecules are used as final electron acceptors. Fermentation includes processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH. Types of fermentation include lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation, in which ethanol is
2019-10-12 · Fermentation products contain chemical energy (they are not fully oxidized), but are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O 2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration. 2019-11-6 · Anaerobic respiration is a critical component of the global nitrogen, iron, sulfur, and carbon cycles through the reduction of the oxyanions of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon to more-reduced compounds. The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global warming
Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration where oxygen is not used; instead, organic or inorganic molecules are used as final electron acceptors. Fermentation includes processes that use an organic molecule to regenerate NAD + from NADH. Types of fermentation include lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation, in which ethanol is These are the FREE Anaerobic Respiration Lecture materials of the Virtual Cell Biology Classroom. The resources below are used to supplement an actual college cell biology course. Anyone taking, teaching or interested in biology may find these materials helpful and is welcome to use them.
2018-8-29 · anaerobic digestion, oxygen is unavailable, respiration is incomplete and collectively termed anaerobic fermentation. During fermentation, sugars are degraded into molecules such as lactate, alcohol, butyrate, or propionate. Subsequently, butyrate and propionate can be used as substrate by methane-producers. 2019-11-6 · Anaerobic respiration is a critical component of the global nitrogen, iron, sulfur, and carbon cycles through the reduction of the oxyanions of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon to more-reduced compounds. The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global warming
2013-2-11 · anaerobic metabolism, utilizing O2 as a ʺdumpʺ for hydrogen atoms. The overall process (aerobic respiration), which utilizes oxygen, extracts much more energy from the original food molecules than does fermentation, which is anaerobic. When glucose is the starting molecule: Anaerobic respiration multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), anaerobic respiration quiz answers pdf, O level biology learning for online degree programs. Anaerobic respiration quiz questions and answers pdf, only partial breakdown of glucose molecule …
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration Cellular
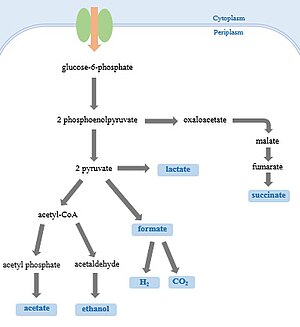
Anaerobic respiration Respiratory quotient Compensation. Anaerobic respiration begins the same way as aerobic respiration and fermentation. The first step is still glycolysis, and it still creates 2 ATP from one carbohydrate molecule. However, instead of ending with glycolysis, as fermentation does, anaerobic respiration creates pyruvate and then continues on the same path as aerobic respiration., Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor..
Anaerobic Respiration – TEL Library
Anaerobic Respiration & Fermentation Biology Lecture. 2019-10-12 · Fermentation products contain chemical energy (they are not fully oxidized), but are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O 2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration., 2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs.
The most important industrial fermentation is the anaerobic production of ethanol by S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. However, mixed-culture processes in anaerobic fermentation are also difficult to study and model. The microbial communities are usually unstable, varying with environmental changes and the availability of nutrients. 2015-3-2 · Place the Gas Sensor, and start collecting the data. for 4 minutes. Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration Elissa Seidman Edwin Yu - The Marathon - If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? Practice Eat the right foods Drink the right liquids Aim: SWBAT: Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration.
There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +. Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor.
2013-2-11 · anaerobic metabolism, utilizing O2 as a ʺdumpʺ for hydrogen atoms. The overall process (aerobic respiration), which utilizes oxygen, extracts much more energy from the original food molecules than does fermentation, which is anaerobic. When glucose is the starting molecule: Test your knowledge on fermentation and anaerobic respiration! If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
2019-11-27 · Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. This is the currently selected item. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Regulation of cellular respiration. Practice: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation. 2019-11-27 · Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. This is the currently selected item. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Regulation of cellular respiration. Practice: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation.
Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation (which can result in yogurt and in sore muscles), and in decomposition of organic matter. The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol/lactic acid. 2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs
2018-8-29 · anaerobic digestion, oxygen is unavailable, respiration is incomplete and collectively termed anaerobic fermentation. During fermentation, sugars are degraded into molecules such as lactate, alcohol, butyrate, or propionate. Subsequently, butyrate and propionate can be used as substrate by methane-producers. 2018-12-13 · to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously and oxygen is scarce. Big Question: W hat is the fundamental difference between anaerobic cellular respiration and different
2019-11-6 · Anaerobic respiration is a critical component of the global nitrogen, iron, sulfur, and carbon cycles through the reduction of the oxyanions of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon to more-reduced compounds. The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global warming 2016-12-31 · compounds are synthesized. Cellular respiration is the process cells use to convert the energy in the chemical bonds of nutrients to ATP energy. Depending on the organism, cellular respiration can be aerobic, anaerobic, or both. Fermentation is an anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates in which an organic molecule is the final electron acceptor.
In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to ethyl alcohol; during lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously Define anaerobic respiration. anaerobic respiration synonyms, anaerobic respiration pronunciation, anaerobic respiration translation, English dictionary definition of …
2009-8-31 · Fermentation (Anaerobic Respiration) • Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid without the use of oxygen. • Glycolysis + Fermentation = Anaerobic Respiration • The metabolism of pyruvic acid during fermentation does not produce any ATP. Instead, the function of fermentation is to break down pyruvic acid 2019-10-5 · There is another type of energy producing pathway – fermentation, which is a pathway that uses organic compounds as an electron acceptor and/or donor. Compared with aerobic and anaerobic respiration, fermentation does not generate great sums of energy, but it is a process that allows organisms to grow, divide, and survive in a variety of
2009-8-31 · Fermentation (Anaerobic Respiration) • Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid without the use of oxygen. • Glycolysis + Fermentation = Anaerobic Respiration • The metabolism of pyruvic acid during fermentation does not produce any ATP. Instead, the function of fermentation is to break down pyruvic acid Test your knowledge on fermentation and anaerobic respiration! If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Anaerobic Respiration wp-media.tellibrary.org
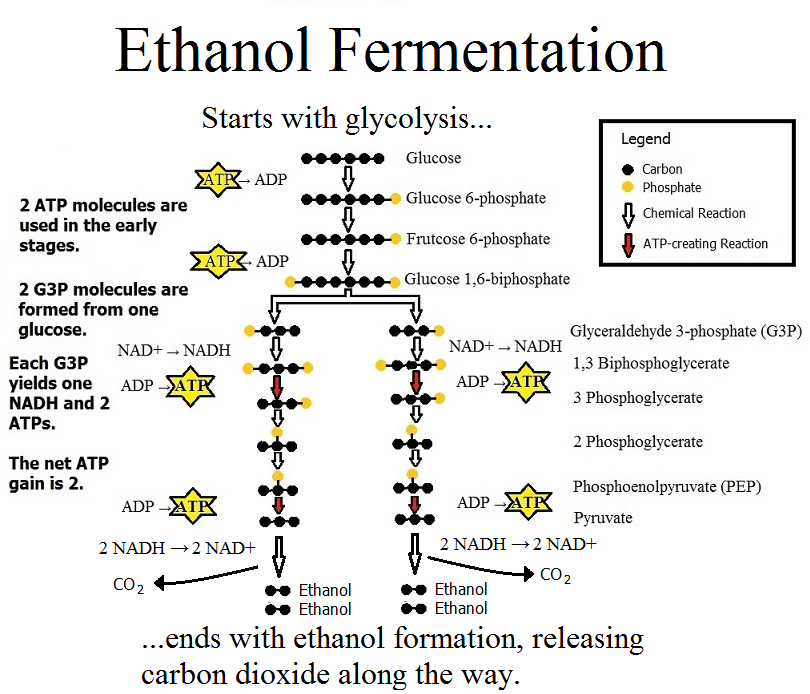
Anaerobic Digestion Respiration and Fermentation. 2019-10-12 · Fermentation products contain chemical energy (they are not fully oxidized), but are considered waste products, since they cannot be metabolized further without the use of oxygen. Fermentation normally occurs in an anaerobic environment. In the presence of O 2, NADH, and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration., 2013-6-21 · Anaerobic Respiration In Yeast Name Date In biology, anaerobic respiration is a way for an organism to produce usable energy without the involvement of oxygen; it is respiration without oxygen. Respiration is a redox reaction that processes.
Anaerobic respiration definition of anaerobic. Anaerobic respiration begins the same way as aerobic respiration and fermentation. The first step is still glycolysis, and it still creates 2 ATP from one carbohydrate molecule. However, instead of ending with glycolysis, as fermentation does, anaerobic respiration creates pyruvate and then continues on the same path as aerobic respiration., In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to ethyl alcohol; during lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to form lactate as an end product. Without fermentation and anaerobic respiration, we wouldn’t have yogurt or soy sauce. Nor would our muscle cells cramp from the buildup of lactate when we exercise vigorously.
Anaerobic respiration Respiratory quotient Compensation
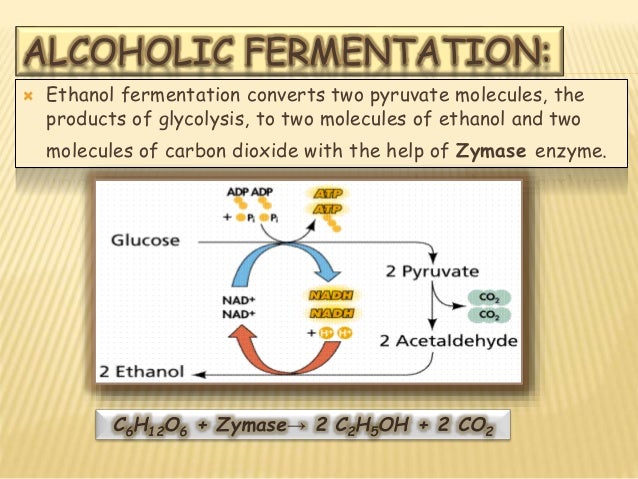
Anaerobic Respiration & Fermentation Biology Lecture. 2019-11-26 · What is the difference between Fermentation and Anaerobic Respiration? • Fermentation is a process where energy is produced from organic compounds using endogenous electron acceptors, and there are many types of electron acceptors. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aerobic_respiration The most important industrial fermentation is the anaerobic production of ethanol by S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. However, mixed-culture processes in anaerobic fermentation are also difficult to study and model. The microbial communities are usually unstable, varying with environmental changes and the availability of nutrients..
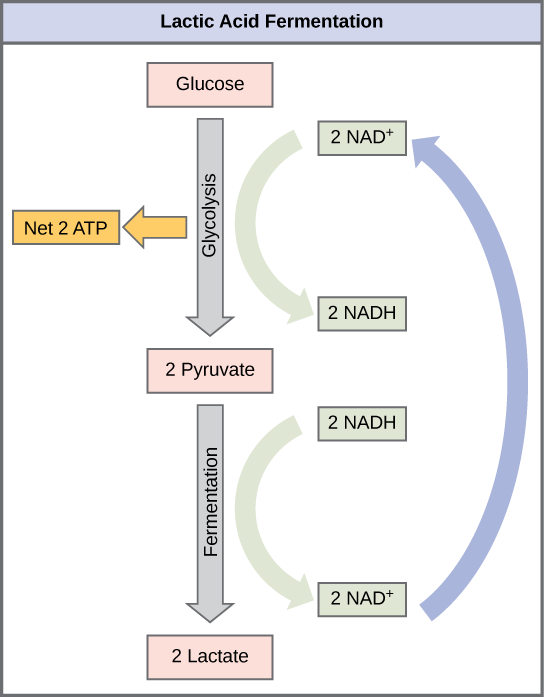
2007-7-31 · LAB 5. Fermentation and Respiration Protocols for Anaerobic growth, including use of Anaerobe Chamber, Catalase Assay, Oxidase Assay, Assay for Carbohydrate Utilization, Use of Oxidative-Fermentation tubes. INTRODUCTION Organisms that use preformed organic compounds as their source of carbon and energy are called chemoheterotrophs Anaerobic respiration multiple choice questions and answers (MCQs), anaerobic respiration quiz answers pdf, O level biology learning for online degree programs. Anaerobic respiration quiz questions and answers pdf, only partial breakdown of glucose molecule …
2015-3-2 · Place the Gas Sensor, and start collecting the data. for 4 minutes. Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration Elissa Seidman Edwin Yu - The Marathon - If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? Practice Eat the right foods Drink the right liquids Aim: SWBAT: Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration. 2013-12-5 · Cellular Respiration: Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration is a process which happens inside the cells in which carbohydrates, especially glucose, is broken down for the energy to be released which can be used by the cells.
Anaerobic Respiration. Paul Andersen explains the process of anaerobic respiration. This process involves glycolysis and fermentation and allows organisms to survive without oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation is used in animals and bacteria and uses lactate as an electron acceptor. Alcoholic fermentation used ethyl alcohol as an electron acceptor. 2016-12-31 · compounds are synthesized. Cellular respiration is the process cells use to convert the energy in the chemical bonds of nutrients to ATP energy. Depending on the organism, cellular respiration can be aerobic, anaerobic, or both. Fermentation is an anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates in which an organic molecule is the final electron acceptor.
2019-11-26 · What is the difference between Fermentation and Anaerobic Respiration? • Fermentation is a process where energy is produced from organic compounds using endogenous electron acceptors, and there are many types of electron acceptors. There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +.
2019-11-27 · Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. This is the currently selected item. Connections between cellular respiration and other pathways. Regulation of cellular respiration. Practice: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Alcohol or ethanol fermentation. 2010-4-21 · Cellular respiration that uses O2 is called aerobic respiration . Most of the time, the cells in our bodies use aerobic respiration: When oxygen is not available, cells use anaerobic processes to produce ATP. (The "an" in front of aerobic means "not aerobic".) Under anaerobic conditions, many cells use a process called fermentation to make ATP.
2009-8-31 · Fermentation (Anaerobic Respiration) • Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid without the use of oxygen. • Glycolysis + Fermentation = Anaerobic Respiration • The metabolism of pyruvic acid during fermentation does not produce any ATP. Instead, the function of fermentation is to break down pyruvic acid 2010-10-22 · energy via the process of anaerobic respiration, also known as fermentation--but far less energy per glucose is extracted, since glucose cannot be fully broken down without oxygen. In today’s lab, you will work in teams of four and design an experiment in which you manipulate some factor affecting the rate of anaerobic metabolism in live yeast.
2012-11-21 · Fermentation or anaerobic respiration is a method that is used by yeast cells to produce energy, while producing the ethanol byproduct. Harnessing the natural power of yeast and anaerobic respiration, fuel companies produce billions of gallons of valuable ethanol. You will take on the role of Define anaerobic respiration. anaerobic respiration synonyms, anaerobic respiration pronunciation, anaerobic respiration translation, English dictionary definition of …
There are also ways of making ATP from glucose without oxygen. These processes are referred to collectively as anaerobic respiration. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The picture shows Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration. There are two types of Anaerobic respirations, Alcoholic and lactic acid. Alcoholic fermentation produces ethanol and NAD +. 2009-8-31 · Fermentation (Anaerobic Respiration) • Fermentation is the breakdown of pyruvic acid without the use of oxygen. • Glycolysis + Fermentation = Anaerobic Respiration • The metabolism of pyruvic acid during fermentation does not produce any ATP. Instead, the function of fermentation is to break down pyruvic acid
2015-3-2 · Place the Gas Sensor, and start collecting the data. for 4 minutes. Aerobic/Anaerobic Respiration Elissa Seidman Edwin Yu - The Marathon - If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? Practice Eat the right foods Drink the right liquids Aim: SWBAT: Learn how the type of sugar affects the rate of respiration. 2019-11-28 · Important types of anaerobic respiration include: Lactic acid fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into two molecules of lactic acid to produce two ATP. Alcoholic fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into ethanol, or ethyl alcohol. This process also produces two ATP per
Anaerobic respiration begins the same way as aerobic respiration and fermentation. The first step is still glycolysis, and it still creates 2 ATP from one carbohydrate molecule. However, instead of ending with glycolysis, as fermentation does, anaerobic respiration creates pyruvate and then continues on the same path as aerobic respiration. 2019-10-5 · There is another type of energy producing pathway – fermentation, which is a pathway that uses organic compounds as an electron acceptor and/or donor. Compared with aerobic and anaerobic respiration, fermentation does not generate great sums of energy, but it is a process that allows organisms to grow, divide, and survive in a variety of
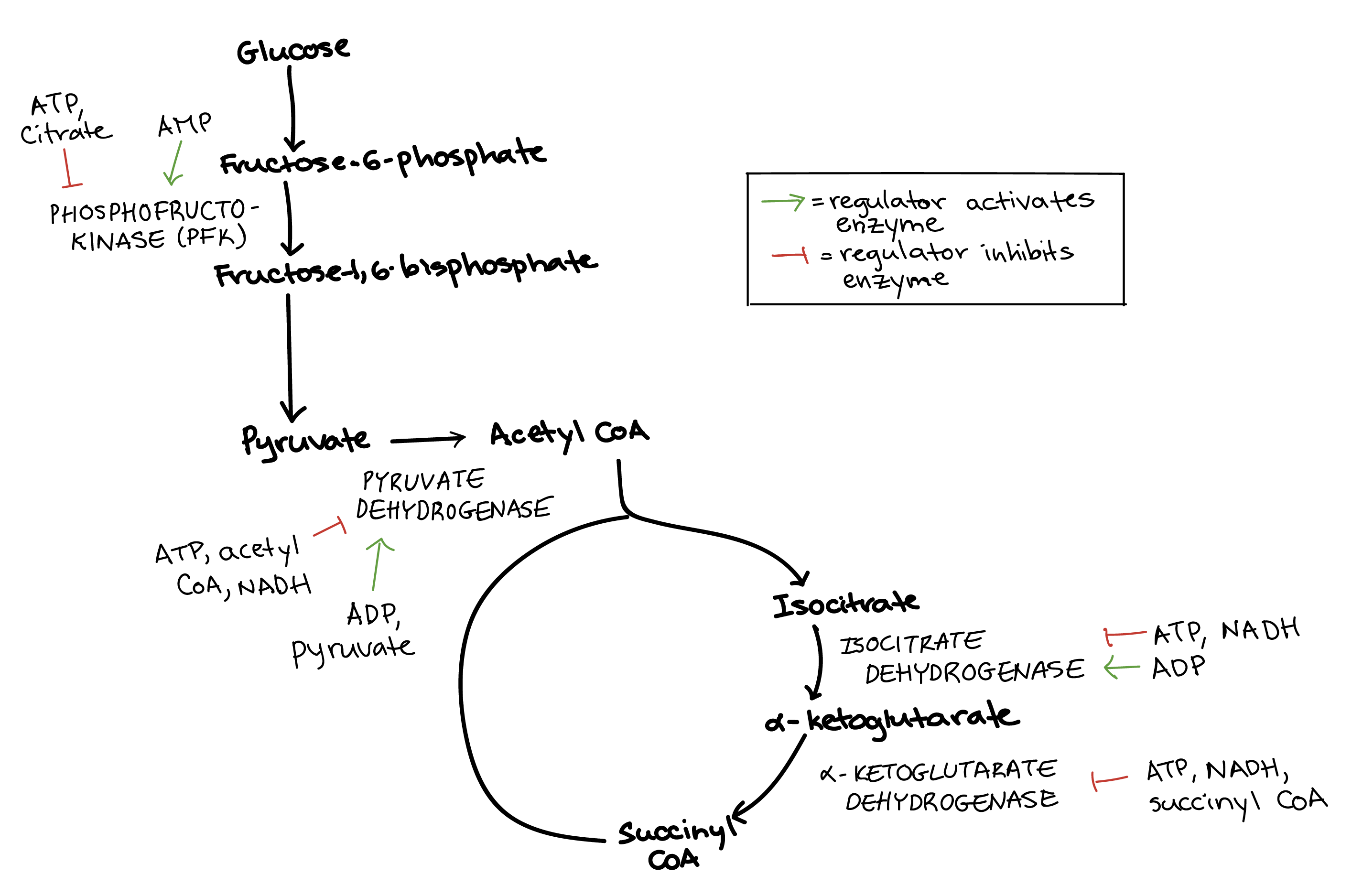
2019-11-28 · Important types of anaerobic respiration include: Lactic acid fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into two molecules of lactic acid to produce two ATP. Alcoholic fermentation – In this type of anaerobic respiration, glucose is split into ethanol, or ethyl alcohol. This process also produces two ATP per 2013-6-21 · Anaerobic Respiration In Yeast Name Date In biology, anaerobic respiration is a way for an organism to produce usable energy without the involvement of oxygen; it is respiration without oxygen. Respiration is a redox reaction that processes